In 2013, the demand for China's auto market was about 20.8 million, with a growth rate of 7%. It is estimated that the total number of vehicles in China will reach 23.5 million by 2015 and 25 million by 2020. The development of automobiles is developing in the direction of high power output, lightweight, high performance, long life, noise reduction, smooth operation, safety and reliability, environmental protection, energy conservation, economical low cost, easy processing, and many varieties. Steel for automotive parts is a key part of automobiles and is a manufacturing material that ensures the core components of automotive performance. The development direction of the automobile puts forward higher requirements for the development of steel for auto parts.
Product Requirements: High toughness, high precision, energy-saving and environmentally-friendly steel for automotive parts applications in the four major automotive systems:
Engine system steel: The engine is the source of the car's power. Among them, crankshafts, connecting rods, cams, and other typical parts are mainly non-quenched and tempered steels, fuel injection systems are mainly used for oil pump nozzles, and valve steels are mainly valve steels.
Transmission and transmission system steel: Transmission and transmission system is the soul of a car, which gear ring, gear hub, gear, gear shaft to gear steel. The transmission system is more like the waist and spine of animals, including transmission shafts, axle shafts, front axles, etc. The steel used for transmission shafts is mainly used.
Suspension and steering system steel: Suspension system is the car's legs, including the suspension spring, stabilizer bar, torsion bar, shock absorbers, etc., mainly spring steel. The steering system is the driving direction of the car, including universal joints, ball heads, steering gears, wheels, bearings, etc. The hubs and bearings are mainly made of bearing steels, and the universal joints, ball heads, and steering gears are mainly gear steels.
Standard system steel: The main use of cold heading steel for fasteners.
Automotive industry application system requirements: Automotive components have the characteristics of high performance, long life, easy processing, low noise, high surface accuracy, and high strength; to achieve lightweight and compact cars, and to reduce CO2 emissions by improving efficiency.
The automotive industry's requirements for materials are: high-strength toughness, easy cutting, high dimensional accuracy, low alloying, environmental friendliness, and omission of heat treatment. The common development trend of the development of steel materials for auto parts is shown in the attached table.
Technology Trends: Accurate control, uniform composition, and micro-alloyed automotive science and technology advancements have driven the development of auto parts technology, and the development of parts and components technology has promoted the scientific and technological progress and technological innovation of automobiles.
High-quality gear steel, high-quality spring steel, high-quality non-quenched and tempered steel, high-quality fastener steel, high-quality bearing steel, and high-quality valve steel are the requirements for the use of special alloy steel in automobile parts. Key material representative. High-quality special steel for automotive parts has been developed toward lightweight, high performance, long life, stable operation, low noise, safety, energy saving, low cost, easy processing, and many varieties. The development direction of the technical quality of high-quality special steel for automotive parts is steel high toughness, high purity, high uniformity, ultrafine grain size, high surface quality, long fatigue life.
The development trend of high quality gear steel. High-quality gear steel has been continuously developed in terms of diversified varieties, easy cutting, environmental protection, low alloying cost reduction, low noise, smooth operation, good steel homogeneity, and small heat treatment distortion.
The technical quality characteristics of gear steels are evaluated in terms of hardenability, purity, grain size, and band structure.
The level of hardenability and the stability of the hardenability value are important indicators for evaluating the quality of gear steel. The goal of hardenability control is 3HRC.
The influence of the cleanliness of gear steel on the fatigue life of gears has drawn increasing attention. The presence of oxides and sulfides in the steel, as well as harmful elements such as N, H, O, P, S, etc., will reduce the mechanical properties of steel, deterioration of the steel's process performance, thus affecting the car's carburizing gear life. The goal of the gear steel oxygen content control is [O]10ppm. It is forbidden to add Ti and Ca in high-quality gear steels, and 0.01% Ti and Ca 0.0005% of steel are specified. The pursuit of non-metallic inclusions is the goal of A2, B2, C1, and D1.
Grain size is an important indicator of gear steel. The fine and uniform austenite grains in the gear steel are quenched to obtain a fine martensite structure, which obviously improves the fatigue performance of the gear, and at the same time reduces the deformation of the gear after heat treatment. The fine uniform austenite grain size has a special contribution to the strength and toughness of the part. In particular, it is of great significance to improve the fracture toughness of gears and enhance the brittle fracture resistance of gears. Gear steel grain size 6 is required. At present internationally in order to obtain high temperatures (>
960 °C) carburizing gear steel, adding or compounding microalloying elements such as Nb, V, Zr etc. during smelting to form alloy carbonitrides in the steel, and the grain size of the steel is 8.
Banded tissue is a structural defect of steel. In the case of gear steel, severe belt-like structures will affect the uniformity of carburizing, increase the degree of quench deformation, and make the carburized gears have poor dimensional accuracy. Therefore, the goal of the control of the ribbon steel structure of gear steel is not more than two.
The development trend of high quality non-quenched and tempered steel. Non-quenched and tempered steel is the addition of micro-alloying elements (V, Ti, Nb, Al, B, or N) to medium- and low-carbon steels or medium- and low-carbon manganese steels. The controlled precipitation (forging) controlled cooling process makes full use of precipitation. Strengthening, fine-grained strengthening and transformation strengthening, etc., make the steels do not need quenching and tempering after hot rolling (forging), and its strength and hardness can reach the level of quenched and tempered steel, at the same time, it has certain plasticity and toughness of high-efficiency energy-saving steel. Non-tempered steel is an environmentally friendly steel that meets both high performance and low cost requirements.
The selection of steel materials for crankshafts, connecting rods, front axles, axles, I-beams, steering knuckles, knuckle arms, camshafts, etc., presents the trend of gradually replacing quenched and tempered steels with non-quenched and tempered steels. Among them, from the viewpoint of reducing the number of processing steps and increasing the productivity, the selection of steel materials for connecting rods is in the trend of gradually replacing the non-stretching materials with the breaking materials.
The characteristic values ​​for evaluating the quality of non-quenched and tempered steel include carbon equivalent, carbon segregation, oxygen content, grain size, decarburization layer, mechanical properties, ferrite content, and inclusion level. For example, the goal of carbon equivalent range control is 0.02%. The goal of carbon segregation control for the entire steel section is 0.03%. The goal of austenite grain size control is not to be thicker than 8 levels. The microstructure should be pearlite + ferrite. The decarburization layer requires that the decarburization depth (ferrite + transition layer) control on each side of the steel be 0.5% of the steel diameter. The goal of oxygen content control is 15ppm. The pursuit of strip control is 1.5.
The development trend of high quality spring steel. The two most important factors affecting the design stress of the spring are the fatigue resistance and the anti-rebound performance, which have become the subject of research and development of spring steels. At present, spring steel steel grades are developing in the direction of economy and high performance. The new generation ultra-high strength spring steel has the following characteristics: ultra-high strength-ductile plasticity, ie, tensile strength 2000 MPa, reduction in area of ​​50%; high fatigue strength and Corrosion fatigue performance; excellent resistance to rebound.
In addition, high-quality spring steel requires good economics. The research and development of its new type of steel, on the one hand, by optimizing the content of alloy elements in the existing spring steel and adding micro-alloying elements, reducing the carbon content and adding V and Nb, etc.; on the other hand is basically not in the existing steel species In the case of change, ultra-high strength can be achieved on the premise of ensuring economical efficiency through processes such as deformation heat treatment, induction heat treatment, and on-line heat treatment. At present, foreign deformation heat treatment and induction heat treatment process have been widely used in actual production, so that online spring steel wire after oil quenching - tempering heat treatment process.
The development trend of high quality cold heading steel. The automotive industry is increasingly demanding high-precision, high-strength fasteners, steel structural joints and non-standard shaped parts. Therefore, the demand for high-purity, high-performance, high-quality cold crucible steel is also more urgent. Technical progress has played a key role in transforming fasteners into highly versatile automotive parts.
The development direction of cold crucible steel is non-quenched and tempered steel, boron steel and ultra-fine grain steel, and non-heat-treated non-heat-treated cold crucible steel has attracted much attention. The non-quenched and tempered cold crucible steel adopts the methods of strengthening and toughening such as microalloying and controlled rolling and cooling. In the process of processing the fastener, the spheroidizing annealing before the cold drawing and the quenching and tempering after forming can be omitted, and the reduction can also be reduced. The decarburization tendency of the threaded part increases the yield.
The characteristic values ​​for evaluating the technical quality of high-quality cold heading steel include cold heading, decarburization layer, and surface quality. The goal of cold heading control is 1/5, and the goal of the decarburization layer control is the 0.3% D diameter of the decarburized layer in the hot rolled state.
The development trend of high quality bearing steel. Bearing steel is mainly used to manufacture rolling elements and rings for rolling bearings. Bearings should have characteristics such as long life, high accuracy, low heat generation, high speed, high rigidity, low noise, high wear resistance, etc. Therefore, bearing steels are required to have high hardness, uniform hardness, high elastic limit, high contact fatigue strength, Required toughness, certain hardenability, corrosion resistance in atmospheric lubricants. In order to achieve the above-mentioned performance requirements, the chemical composition uniformity of bearing steel, the content and type of non-metallic inclusions, the particle size and distribution of carbides, and decarburization are demanding. Bearing steels generally develop in the direction of high quality, high performance and variety.
Evaluating the quality of bearing materials depends primarily on the purity and uniformity of the material. The purity of the material means that the inclusions in the material are as small as possible. The homogeneity of the material means that the inclusions and carbide particles in the material are fine and diffuse. Specifically, bearing steels mainly develop in both directions of high cleanliness and performance diversification. Increasing the cleanliness of the bearing steel, in particular reducing the oxygen content in the steel, can significantly extend the life of the bearing. The goal of the oxygen content control of the bearing steel is 5ppm. The goal of the oxide inclusion control in steel is 10m for inclusion size, 5ppm for titanium content control, and 30ppm for nitrogen content control.
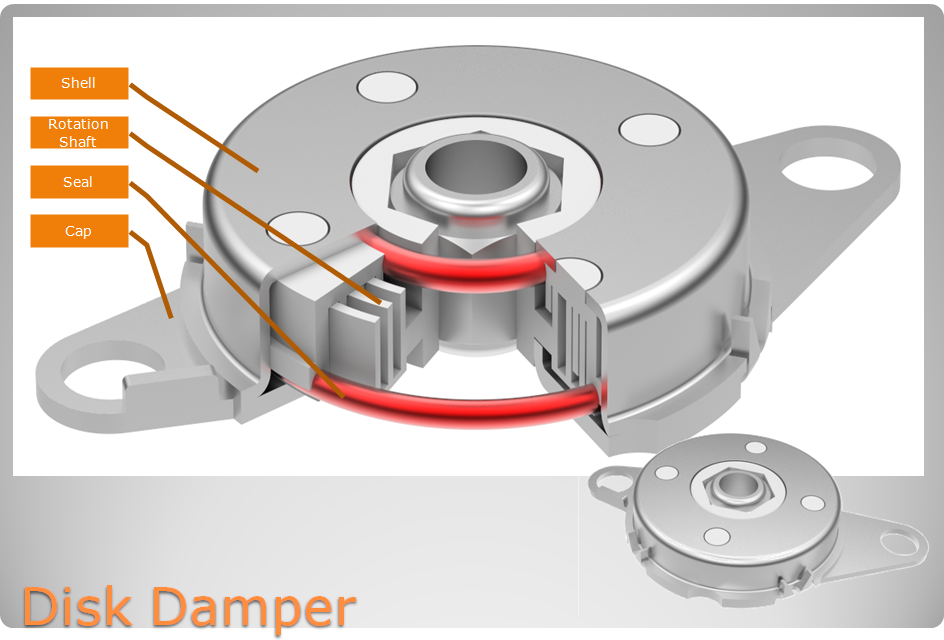
Flat disk Rotary Damper mainly used for large diameter, small height space. Disk dampers provide energy absorption and rotational deceleration. We offer many different models from mild to extreme. Our disk dampers are the perfect solution for a wide range of applications, from scanner, and glove boxes to auditorium seating to. Disk dampers are designed to control and smooth out the opening and closing of lids, and doors.
Our damper is conducive to performing structural movement in soft, silent and safe environment, mitigating impact load, avoiding strike damage, prolonging mechanical life, reducing noise disturbance, improving product quality and improve customer satisfaction.
NOTE:
1. Please contact the corresponding product engineer for specific torque products.
2. Max. rotation speed: 50r/min
3. Max. circle rate: 6 cycle/min ( Clockwise360 °, 360 ° anti-clockwise for 1 cycle)
4. Operating temperature: -10~50℃
5. Storage temperature:-30~80℃
| NO. | Description | Material |
| 1 | Shell | SPFC |
| 2 | Cover | SPFC |
| 3 | Shaft | PA/POM |
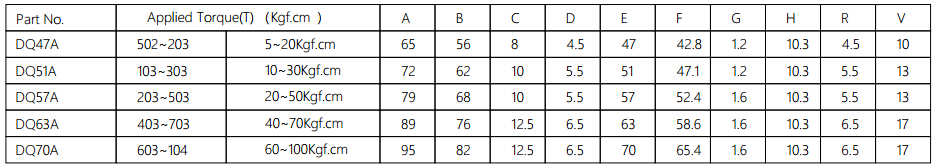
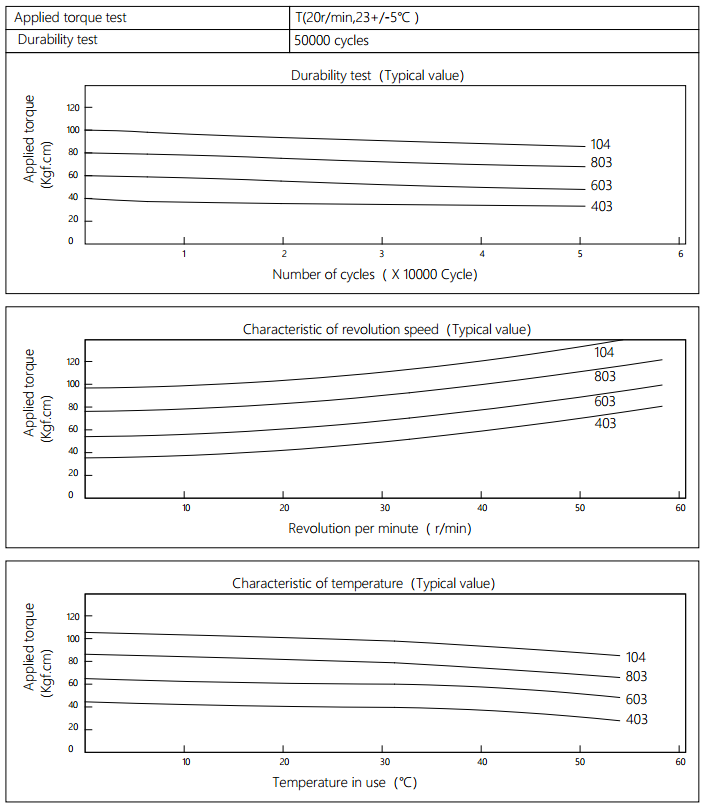
Applied torque:(T)
Test Temperature: 23+/-5℃
Rotating speed: 20r/min
Durability test Metho: Clockwise 360 °, 360 °anti-clockwise
Rotating speed: 20r/min
Test Frequency: (1cycle/min)
Test Temperature: 23±5℃
Durability test cycle: 50000 cycle
Test result criteria: Store in the room temperature for 24 hours or more after the test, recording to the torque T=T±30%T.
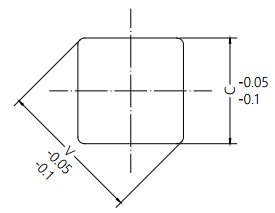
The damper square hole coordinateswith the rotation axis dimension tolerance.
Disk Damper,Adjustable Dampers,Excavator Disk Damper,Spare Disk Damper,Oval Disk Damper
Shenzhen ABD Equipment Co., Ltd. , http://www.abddamper.com